4 min read
Uses of Metals: Types, Classifications and Applications
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
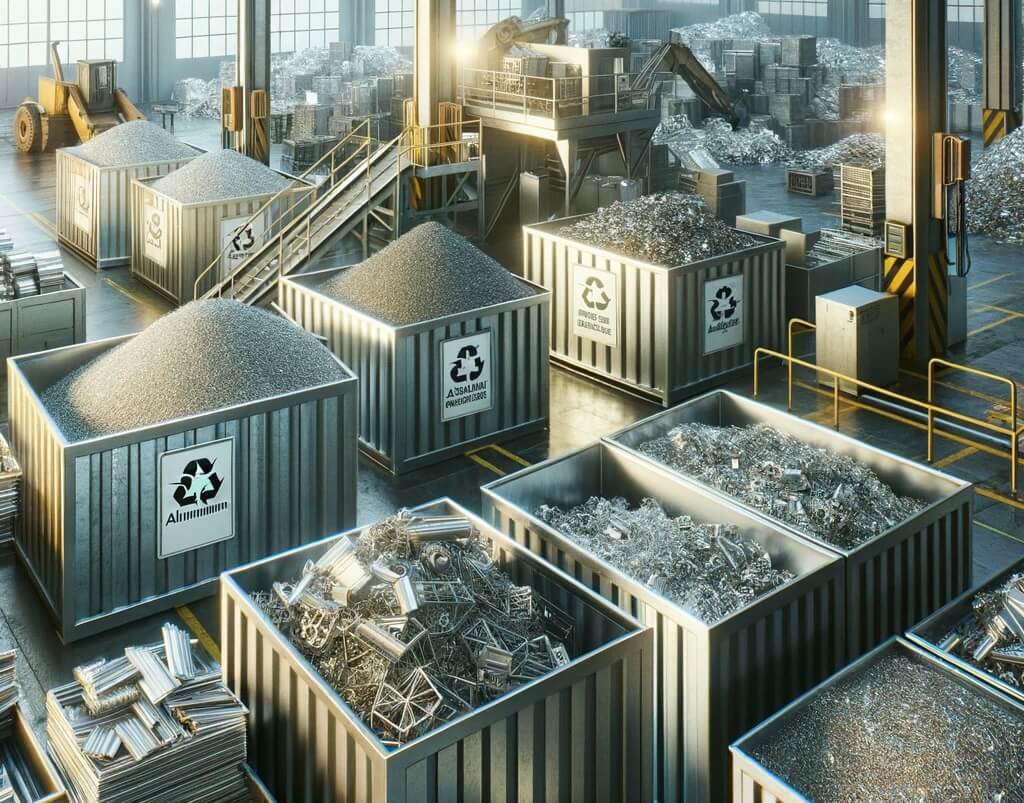

Aluminium recycling is one of the most efficient and environmentally sustainable industrial processes available today.
A key element in waste management and in reducing the consumption of natural resources, it stands as a cornerstone of the modern circular economy.
In the following guide you will find:
- Why Aluminium Recycling Is So Important
- How the Aluminium Recycling Process Works
- Advantages of Aluminium Recycling
- Environmental Impact in Key Sectors
- Future Policies and Technologies
- Weerg and Sustainability in Aluminium Processing
Unlike many other materials, aluminium retains its metallurgical properties even after numerous remelting cycles.
This makes it one of the most sustainable materials available.
The main reasons:
Aluminium is therefore an ideal material for creating circular production chains and reducing the environmental impact of industrial processes.
Aluminium recycling follows a series of well-defined stages, designed to recover and purify the metal efficiently.
Aluminium comes from:
cans
industrial scrap
demolition waste
chips from CNC machining
Separation is carried out through:
eddy current separators
optical sorting
density separation
The material is shredded into small flakes to:
increase heating surface
improve melting efficiency
reduce energy consumption
Thermal or chemical processes remove:
paints
oils
coatings
contaminants
Ensuring a purer, higher-performing material.
The shredded material is melted in furnaces at around 750°C.
During melting:
remaining contaminants are eliminated
alloying elements may be added
Finally, the molten aluminium is transformed into:
ingots
sheets
billets
ready for a new production cycle.

Aluminium recycling is one of the most advantageous processes in both economic and environmental terms.
Aluminium recycling has particularly significant positive effects in three sectors: packaging, automotive and construction.
Beverage cans are among the most recycled products in the world.
Recycling rates:
60–75% in Europe and the United States
95% in Brazil
Every recycled can can power: a 100 W light bulb for 20 hours.
Annual energy savings correspond to the consumption of millions of homes.
Around 90% of aluminium in end-of-life vehicles is recovered.
Benefits:
reduced use of primary aluminium
lower CO₂ emissions
support for the production of lighter, more efficient vehicles
At the end of a building’s life cycle:
60–85% of its aluminium is recycled
Thanks to its durability, aluminium retains all its original properties, making it ideal for continuous reuse.
Environmental policies are accelerating the transition towards even more efficient recycling.
EU targets
The European Union aims for:
Technological innovations
The sector is investing in:
advanced AI-based sorting systems
low-emission furnaces
treatments that reduce greenhouse gases during remelting
more sustainable purification and de-coating processes
The future of aluminium recycling is increasingly efficient, automated and low-impact.

Weerg also integrates sustainable practices in aluminium management within its CNC machining processes.
Main initiatives:
collection and recovery of all aluminium chips generated by milling and turning
sorting and delivery to certified recycling channels
waste reduction through optimised digital processes
continuous monitoring of material usage
a concrete contribution to the metal’s circular economy
Weerg’s production model allows scrap to be minimised, environmental impact reduced and every kilogram of material enhanced.
Aluminium recycling is not just an industrial process: it is a strategic pillar for building a more sustainable economy.
Thanks to its infinite recyclability, 95% energy savings and drastic emissions reductions, aluminium is an essential material for an efficient, circular and responsible future.
With advances in technologies and environmental policies, aluminium recycling will become even more efficient, cleaner and more automated.

4 min read
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
2 min read
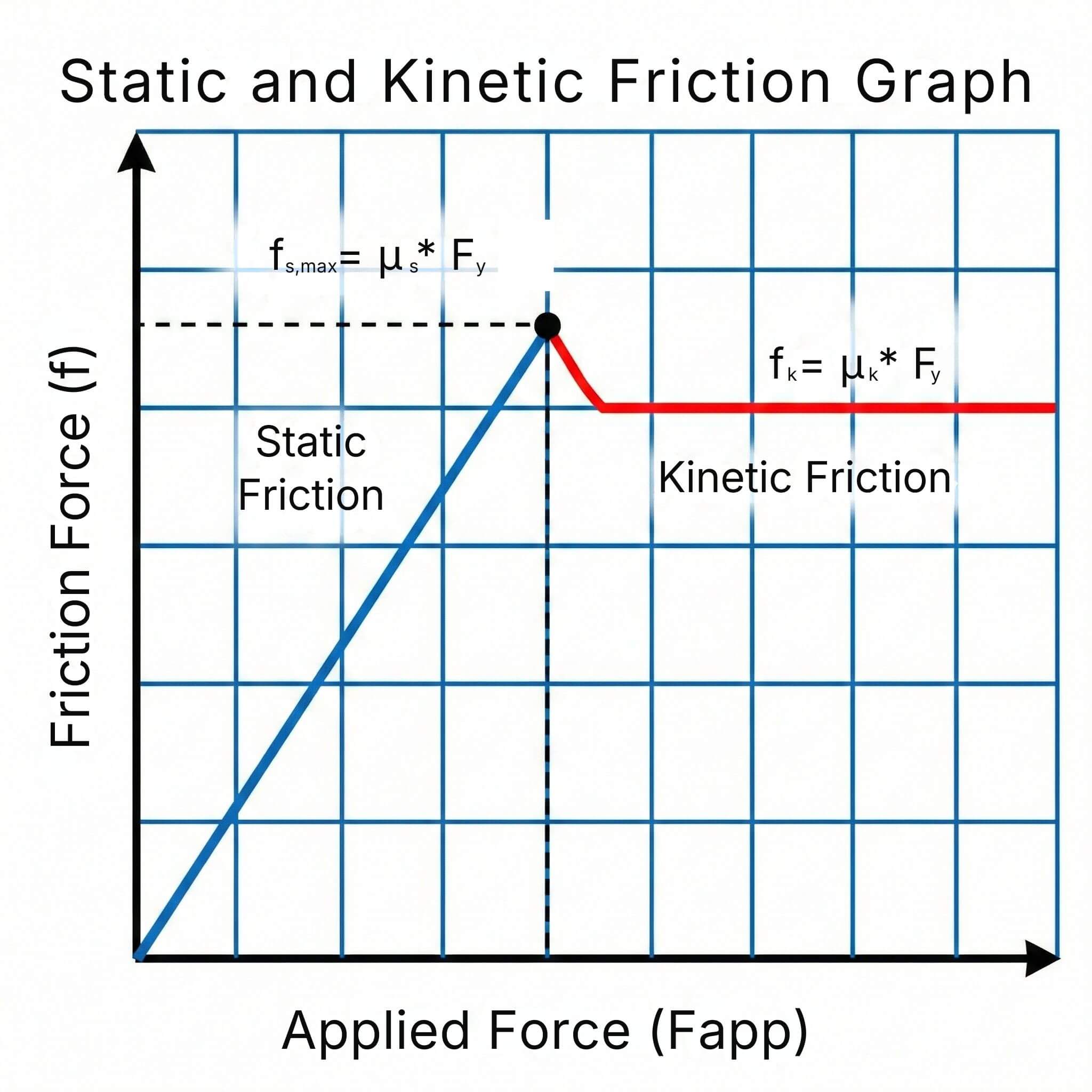
The coefficient of friction (μ) measures the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact. It is a key parameter in mechanical design...

3 min read
The CBAM regulation (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) represents one of the key pillars of the European strategy for industrial decarbonisation...