6 min read
3D Printing and Nanotechnology
3D printing and nanotechnology are two fields of research and innovation that, at first glance, might appear worlds apart. The former focuses on...
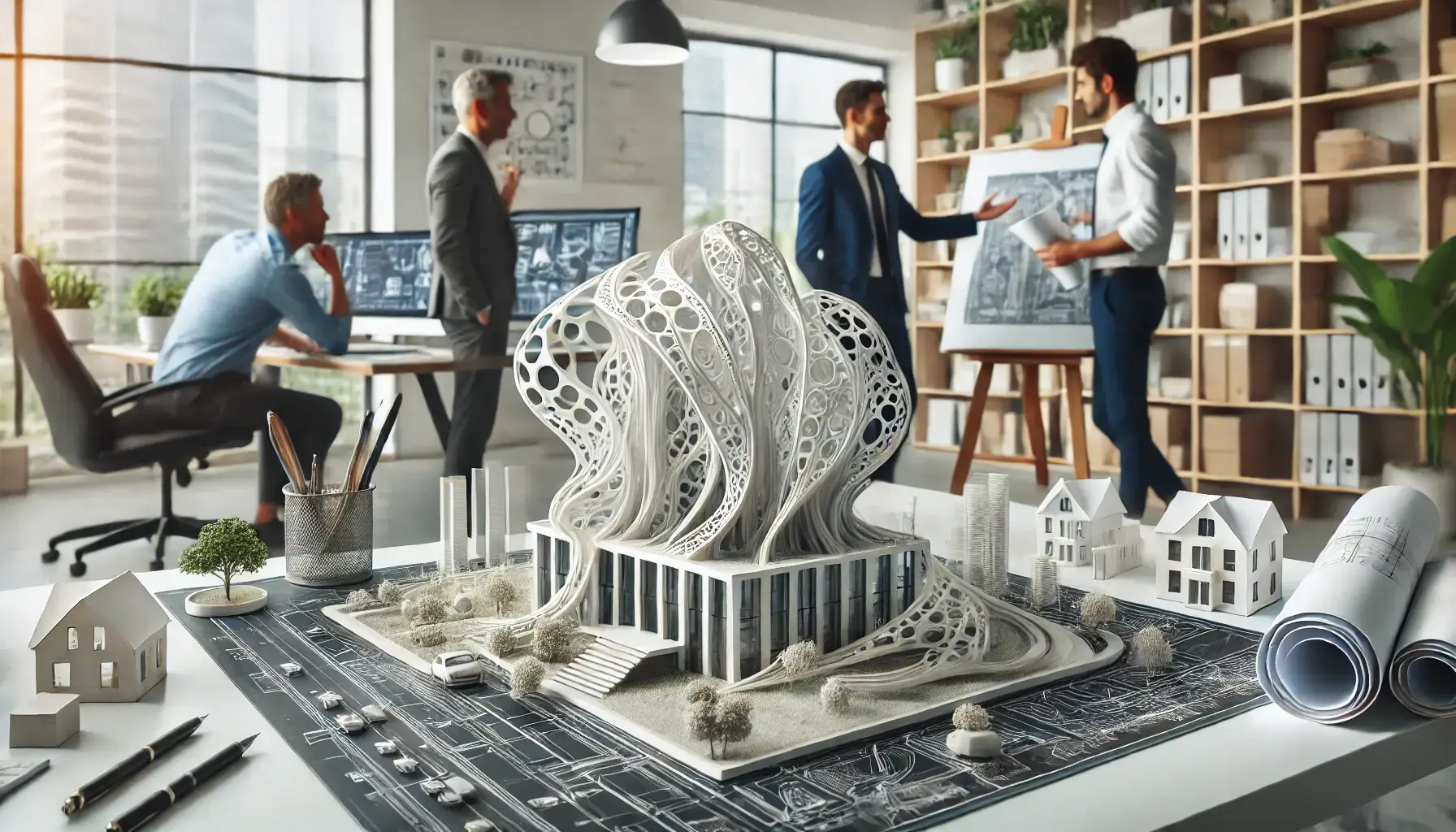

In recent years, 3D printing has revolutionised various industries, and architecture is no exception. Among the most advanced 3D printing technologies in the sector is Multi Jet Fusion (MJF), developed by HP, which enables the creation of detailed and durable models using thermoplastic materials like PA12 nylon. Thanks to its unique qualities, MJF has become an invaluable resource for architectural firms aiming to produce precise and robust prototypes, optimising time and cost while enhancing the quality of design visualisation for clients.
This guide delves into the potential of MJF technology, detailing its functionality, benefits, and specific applications in architecture, from exterior and interior design to detailed urban models. Future prospects, such as the integration of MJF printing into BIM platforms and the development of more sustainable materials, will also be explored to envision an architecture that is increasingly innovative and eco-friendly.
 Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) is one of the most advanced 3D printing techniques for thermoplastics, particularly suited for high-precision projects in sectors like architecture. Developed by HP, it allows the construction of detailed and durable models through the use of PA12 powders, a versatile thermoplastic polymer.
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) is one of the most advanced 3D printing techniques for thermoplastics, particularly suited for high-precision projects in sectors like architecture. Developed by HP, it allows the construction of detailed and durable models through the use of PA12 powders, a versatile thermoplastic polymer.
MJF stands out for its ability to create functional models, suitable not only for prototyping but also for end-use applications. This makes MJF with nylon PA12 an optimal choice for architectural studios seeking to integrate complex components into their designs.
PA12, also known as polyamide 12, is a material with exceptional mechanical and chemical properties. It is robust, impact-resistant, and has a smooth, uniform surface. Its key features include wear resistance and dimensional stability—essential qualities for architectural models that need to endure frequent handling and maintain structural precision.
The MJF process uses a series of print heads to apply a fusing agent and a detailing agent onto layers of PA12 powder. A heating unit then passes over these layers, fusing the material to create the component.
 Rapid and precise layering: This technology enables the creation of high-resolution three-dimensional models, ideal for architects requiring precision and detailed accuracy.
Rapid and precise layering: This technology enables the creation of high-resolution three-dimensional models, ideal for architects requiring precision and detailed accuracy.MJF 3D printing with PA12 is revolutionising how architects approach modelling. The main advantages include:
The versatility of PA12 allows architectural firms to explore various practical applications:
PA12 is a recyclable and reusable material, and the MJF process allows for the reuse of leftover powder in subsequent prints, reducing waste. This makes MJF printing a sustainable option for architecture, increasingly leaning towards eco-friendly, low-impact solutions. Additionally, compared to other modelling materials, PA12 has a lower environmental footprint and can be reused multiple times before disposal.
 While MJF 3D printing offers numerous advantages, some challenges include initial costs, the need for a controlled environment to prevent deformation, and the risk of powder contamination. However, services like Weerg address many of these issues by providing advanced 3D printing solutions that mitigate deformation and contamination risks, optimising processes and making the technology even more accessible and convenient for architectural firms.
While MJF 3D printing offers numerous advantages, some challenges include initial costs, the need for a controlled environment to prevent deformation, and the risk of powder contamination. However, services like Weerg address many of these issues by providing advanced 3D printing solutions that mitigate deformation and contamination risks, optimising processes and making the technology even more accessible and convenient for architectural firms.
The future of MJF printing in architecture could see the development of more sustainable materials and the integration of the technology into BIM (Building Information Modelling) platforms. This would enable more seamless management between digital modelling and physical realisation.
MJF technology with PA12 nylon represents a pivotal innovation for modern architecture, with its capability to produce detailed and durable models. Architects and designers can better visualise their ideas, reducing costs and lead times while enhancing presentation experiences for clients. In a field where visualisation is key, MJF 3D printing offers an ideal combination of precision, flexibility, and sustainability.
As technology evolves, MJF 3D printing could not only become a cornerstone in model production but also transform into a tool for experimenting with and constructing structural components for buildings, paving the way for innovative and sustainable design opportunities.
6 min read
3D printing and nanotechnology are two fields of research and innovation that, at first glance, might appear worlds apart. The former focuses on...

6 min read
Padel has seen exponential growth in Italy and worldwide in recent years. A glance at sports clubs in major cities and smaller towns alike reveals an...

6 min read
The game of chess boasts a history spanning millennia, seamlessly merging art, strategy, and culture into a singular experience that has captivated...