2 min read
Young’s Modulus: What It Is, How It’s Calculated and Why It Matters
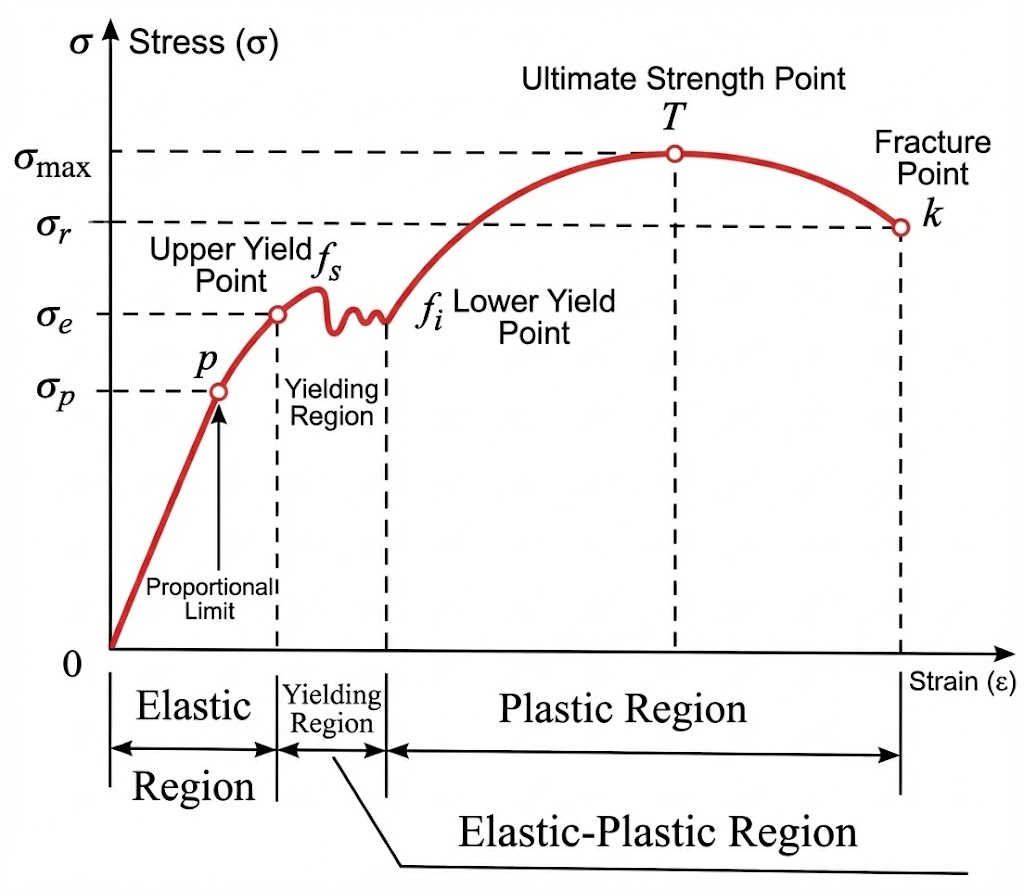
Young’s modulus, also known as the longitudinal modulus of elasticity, is one of the most important mechanical properties of materials. It is used...
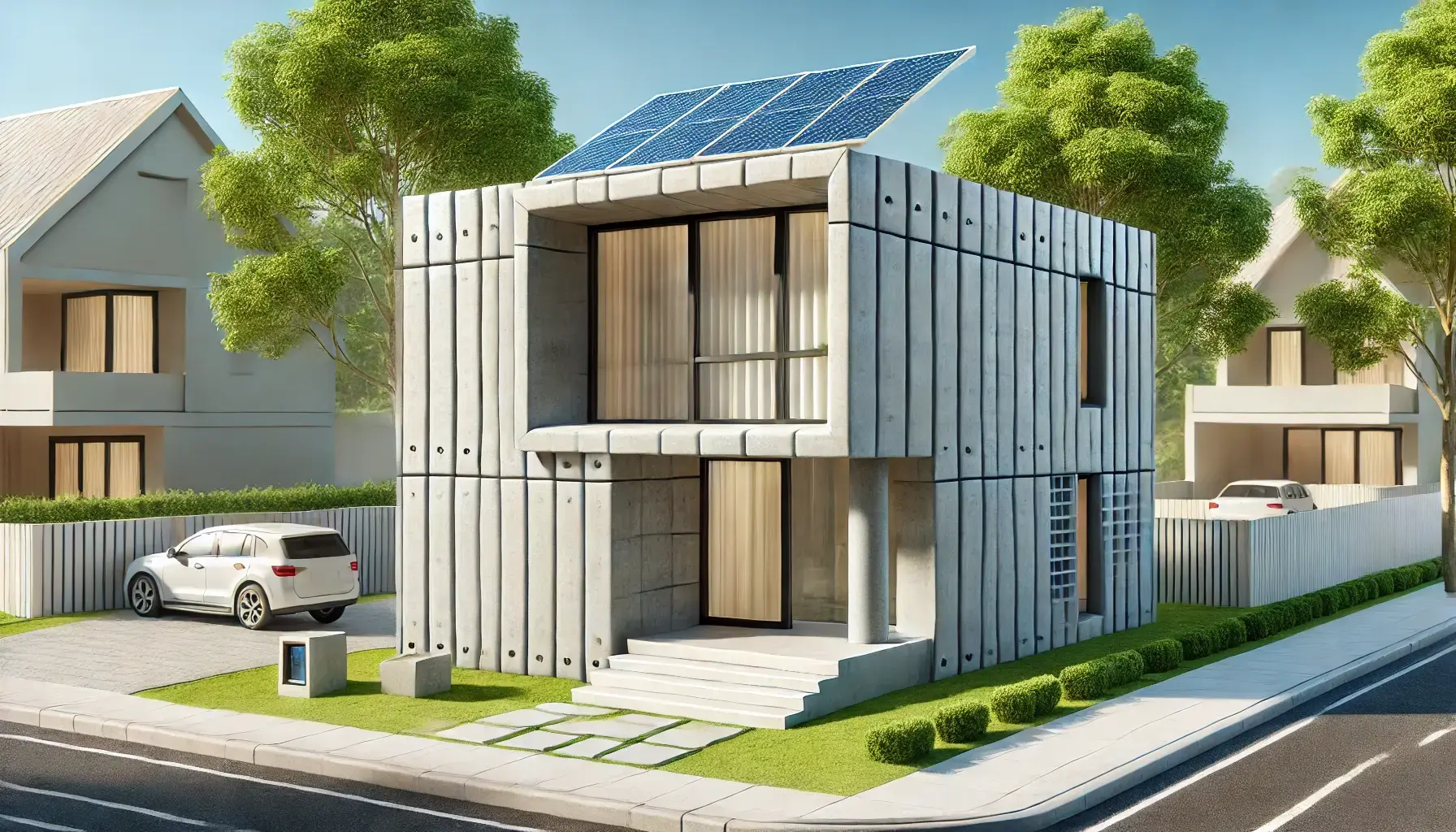

The technology of 3D-printed houses is rapidly transforming the construction industry, bringing with it a mix of excitement and skepticism. But are these homes truly the future or just a passing trend?
One of the most remarkable developments in this field has recently been presented by the University of Maine with the world's largest 3D printer, named Factory of the Future 1.0. This machine uses thermoplastic polymers and can print an entire house in just 80 hours. The printer is capable of creating structures up to 29 meters long, 10 meters wide, and 5.5 meters high, printing at a speed of 227 kilograms of material per hour. Moreover, it can switch between different printing techniques, such as continuous layering for long walls, subtractive manufacturing, and robotic arm operations. What makes it even more interesting is the ability to use a wide range of materials, including wood fiber mixtures.

Photo by CyBe
3D printed houses offer numerous advantages over traditional construction methods. Firstly, they are more cost-effective, significantly reducing labour costs: a printer requires only one operator to function. Additionally, construction is faster: while a traditional house takes months, a 3D printed house can be built in a few days or weeks.
Another positive aspect is environmental sustainability. 3D printing uses only the necessary material, thereby reducing waste. Some projects, such as CyBe Construction in Milan, even use recycled concrete from demolition debris, demonstrating an eco-sustainable approach.
Around the world, various projects are showcasing the potential of 3D printed house. In Texas, the Wolf Ranch project has seen the construction of 100 3D printed homes, each ranging from 140 to 195 square meters. These homes are equipped with solar panels and smart home technology, demonstrating how 3D printed houses can be not only practical but also cutting-edge.
Another significant example is provided by ICON and New Story, who have built 3D printed houses in Texas using a material called Lavacrete, a polymer designed to simulate the properties of cement. These houses, constructed in less than two weeks, demonstrate the speed and efficiency of 3D printing in construction.

Photo by CyBe
Despite the numerous advantages, 3D printed houses still face some challenges. The initial costs for purchasing or renting the printers can be high, and the technology is still being perfected. Additionally, the final cost of a 3D printed house includes not only the materials but also the labor for interior and exterior finishes, as well as the installation of electrical and plumbing systems, which can increase the overall price.
However, as technology advances and costs decrease, 3D printed houses could become a widespread and accessible solution, revolutionising the construction industry and offering new possibilities for sustainable and affordable housing.
In conclusion, 3D printed houses represent an increasingly concrete and promising reality, capable of profoundly transforming our way of building and living. This technology not only offers the possibility of creating homes in record time and at reduced costs but also opens new frontiers in terms of customised design and environmental sustainability. The potential of 3D printing goes beyond housing: today, companies like Weerg allow customers to print a wide range of household items. Among these, chandeliers, electrical plugs, and various domestic accessories have become common products made with 3D printing. This capability offers not only an unprecedented level of customisation but also significant cost and production time reductions. Thanks to 3D printing, consumers can get exactly what they need quickly, without compromising on quality. Weerg, in particular, uses advanced technologies and a wide range of materials, enabling the creation of unique products that perfectly meet individual customer needs.
2 min read
Young’s modulus, also known as the longitudinal modulus of elasticity, is one of the most important mechanical properties of materials. It is used...

3 min read
Galvanisation is one of the most effective and widely used surface treatments for protecting steel and other metals from corrosion, oxidation and...

2 min read
VALOI, a brand of the Finnish company Kameratori Oy and specialised in film-digitalisation systems for the home market, has started a collaboration...